Table of Contents
April 2015, Release 1.6
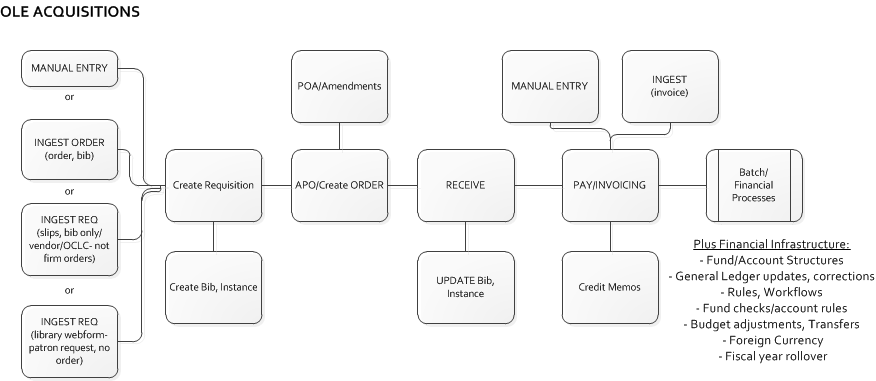
The Select & Acquire module encompasses Financial, Selection, Acquisitions, Receiving, Payment/Invoicing, Licensing, and Electronic Resource Management (ERM), a component that support operational processes for demand-driven acquisitions of library resources. The module manages pre-order and selection of all types of order requests for library materials, and upholds the complete purchasing, receiving and payment operations of ordered library materials. Select & Acquire components also provide workflow design and functionality to encompass print and electronic serials, subscriptions, interval check-in, and productivity reports.
Financial and budgeting structures within the system allow flexibility for library materials to be purchased outright, leased, or licensed. OLE offers fully automated EDI features for direct data exchange with vendors. With the 2.0 release, the ERM component will support the lifecycle of electronic resources and packages including licensing, purchasing, and daily administration. The Global Open Knowledgebase (GOKb), a community-managed knowledge base of subscribed resources, will be tightly integrated with OLE for ingesting and maintaining acquired electronic books and serials.
Select and Acquire Features:
Re-examines library business operations
Focuses on digital-based workflows
Interoperates and integrates with other enterprise and network-based systems
Ability to ingest bibliographic information from Webform
Ability to ingest files of bibliographic records and orders
In the OLE environment, all acquisitions transactions require fund structures, financial processing, and accurate maintenance of the OLE General Ledger. OLE has adapted Kuali Financial System (KFS) Budget Adjustment documents and Fiscal Year End e-documents to manage budgets. OLE uses the adapted KFS Pre-Disbursement Processor (PDP) to export encumbrances, expenses/invoices, credits, and prepayment requests/disbursement vouchers to university financial systems. In a future release, OLE will be developing an import/incoming financial integration tool that allows the library to receive updates from the university financial office.
Financial Features:
Chart of Accounts/Financial Structures
Budget Adjustment, Transfers, Pre-Encumbrance
Accounts: Block, Restrict, SFC, +/-, Fund checks, Access Security
Fiscal Year Rollover transactions
Foreign Currency exchange
Vendor/Publisher record management
Will communicate with campus financial system
Load budgets, account structures
OLE Attributes of Legacy Fund Codes, Stewardship
Acquisitions transactional documents within OLE require a fund to pay for items in the order process. OLE relies on a variety of Chart of Accounts (COA) tables to function. These tables define attributes and values used by the system to validate transactions. They also control the often complex relationships between elements in the Chart of Accounts that must be leveraged for internal and external reporting. For example, tables store basic information such as the sub-fund groups to which new accounts may be assigned and the calendar month that correlates to the first month of your institution's fiscal year. This type of flexibility is one of the features that make OLE a highly configurable application to support Acquisitions.
OLE adds over and under tolerances for encumbrances and for expenses. Sufficient funds checking for encumbrances and expenses are formulated differently within OLE. OLE allows sufficient funds check options like KFS (at Object Code, Object Level, Consolidation, Account, Cash), but also allows users to set a block when the fund check equals the set limit, block/notify within a %/$ range of depletion, or allow overages to a $/%. Sufficient fund checks can occur on Requisitions (REQ), Purchase Orders (PO), Purchase Order Amend (POA), Invoices (PRQS), Payment or Prepayment Requests (PREQ/PPRQ).
Note
To learn more about managing Chart of Accounts and the associated E-documents, see the relevant section of Guide to the OLE Select and Acquire Module.
OLE is adapting the KFS General Ledger (GL) for use in the generation of offsets and the posting of transactions to the balance tables, from various acquisitions transactions. The GL is the official repository for all of OLE financial and budget information. It stores account balance and budget information for multiple fiscal years and stores a detailed record of all financial transactions. Users interact with the GL by creating electronic documents that, when fully approved, are posted to the GL. The OLE General Ledger is a batch processing application that expects all GL pending transactions to be collected in batch form from the GL entry files. The daily batch contains transactions generated in OLE as well as transactions created in external applications and converted to the GL entry format.
Note
To learn more about the General Ledger and the associated E-documents, see the relevant section of Guide to the OLE Select and Acquire Module.
The Financial Processing (FP) component allows users to create and maintain a variety of e-documents (maintenance and transactional), generate reports, and upload data in batch. Many of the financial processing documents are not dependent on other financial processing module documents and independent of other OLE modules. For example, the Disbursement Voucher is for processing payments that are not transacted through the Acquisitions module of OLE.
Note
To learn more about Financial Processing within OLE, see the Others section of Guide to the OLE Select and Acquire Module.
OLE Selection supports procuring decisions that library collection managers, patrons or acquisitions staff make through acquisitions workflows. In OLE, select functions are often considered Pre-orders, wherein Requisitions become placeholders for future acquisitions review. Requisitions are managed through action lists, and the Order Holding Queue.
Selection Features:
Webform allows patrons to enter a request for an item the library does not own
Manual requisition allows staff to create an order for an item
Enhanced Pre-Order selection
Title search capability (Docstore)
Initiate patron requests and workflows
Order Holding Queue
Import Bibliographic records only
Import slips
Note
To learn more about Requisitions and the Order Holding Queue, see the relevant sections in the Guide to the OLE Select and Acquire Module.
To learn more about importing batch records (Batch Framework), see the relevant section of Guide to the OLE System Administration Functions.
The Acquisitions module or purchasing functions encompass all related encumbrance, expense, ordering, receiving, and payment for titles in a variety of formats. Depending on the format, the acquisition of an item may have an associated license/registry that the system is equipped to manage and document as described in OLE Electronic Resource Management Overview- License Requests documentation. Brief bibliographic records are created or edited/linked in the system and an order is created for acquisition. The order is received and paid for upon receipt from the supplier.
The Acquisitions module is used to order, receive and process payments for library materials. Invoices and Credit Memos are sent to the Pre-Disbursement Processing Module (PDP) for disbursement. It includes several e-documents to help libraries manage its acquisitions and accounting processes. OLE users may initiate Requisition e-documents (“Pre-Orders”) to suggest titles for ordering. Fully approved Requisition e-documents are then processed through workflows and become Purchase Orders. Under certain conditions (specified by your library’s business rules in OLE), fully approved Requisitions may become Purchase Orders automatically without any additional processing.
Note
To learn more about Requisitions and Purchase Orders, see the relevant section of Guide to the OLE Select and Acquire Module.
Serials Acquisitions support the selection and acquisitions of continuing resources. OLE accommodates receipts for the variety of publishing schedules - annual or irregular, numbered or unnumbered, monographic or non-monographic books in series.
Serials Acquisitions Features:
DocStore supports Bibliographic record and Instance records: Holdings and Items as well as E-Instances for electronic materials.
Serials single title order
Serial bundles, includes print and electronic versions of title
View and edit subscriptions
Action Interval-based receiving record
Deposits and prepayments
Claiming reports; Unpaid subscriptions reports (scheduled for a future release)
Note
To learn more about Serials Receiving, see the relevant section of Guide to the OLE Select and Acquire Module.
OLE Receiving supports the receiving and cataloging of ordered library materials, as the first step to making library materials available for circulation, following the completion of all required cataloging activities. OLE allows receiving of a quantity and/or parts on line items, as well as offers the ability to report unordered line items, damaged items, or return items. In addition, OLE accepts record annotations such as receiving note(s), and special handling directives.
Receiving Features:
Receiving Queue - global actions promote receiving across Purchase Orders from a single search interface
Combined Receiving, Invoicing - interactions prompt auto or manual processing of Invoice while concurrent Line-Item Receiving
Create additional Item records for each “copy” received
Initial Requisition, Purchase Orders auto-create single items regardless of quantity during ordering
Based on the action-interval established for a title, OLE offers an alternative to line item receiving for serials/journals and optional receiving for multi-part monographs
Receiving staff can update full cataloging records during processing of bibliographic OLE Instance (holding and item) cataloging
Note
To learn more about Monograph Receiving and Receiving and Claiming Queue, see the relevant section of Guide to the OLE Select and Acquire Module.
Serial subscriptions require repeated receiving of individual issues over time--for purposes of “receiving”, serials are distinct from “receiving” non-serials. The latter are typically “received” by changing a PO line item status and that is all that is required for a receiving process. By contrast, serials are typically “received” by recording receipt of individual issues and--since in most libraries unbound current issues are shelved separate from bound older issues--a distinct type of record is required. The Serial Receiving Record allows for action interval checkin.
Note
To learn more about Serials Receiving and action interval checkin within OLE, see the Serials section of Guide to the OLE Select and Acquire Module.
OLE can set maximum receiving thresholds ($) to require reception even if the initial order indicates “no Receiving required”. Receiving Requirements for purchase orders can be set at “yes” or “no” on the Requisition indicating whether receiving is required or not for an item. Based on Receiving Required rules, OLE will run checks that display errors if a user attempts to process Invoice/ Payment Request for quantities greater than quantities actually received.
For items not on the original Purchase Order, users may create Purchase Order Amend (POA) documents. The POA must be processed before an invoice can be approved.
Note
To learn more about how Purchase Order Amend documents currently works in OLE, see the relevant section of Guide to the OLE Select and Acquire Module.
Although OLE technically processes vendor invoices as payment requests, the OLE Invoice document was created to accommodate many-to-one purchase orders to payment requests. This e-document populates payment requests for staff. OLE also processes any negative amounts or credits as separate credit memos. Payments (“paid”) display on purchase order line items. Prorating on Invoices and Payment Requests allows users to take a $500 Shipping & Handling charge (or other types) and optionally assign accounting lines to it (KFS behavior), or prorate it across line items: manually, by quantity, or by dollar amounts. OLE accommodates advance payments to vendors (deposit accounts), and allow a variety of batch jobs, to ensure accurate information to university financial office. Related document links display on purchase orders and payment requests, linking them, plus Receiving and Requisitions.
Payment/Invoicing Features:
Payment schedules are indicated on initiating Purchase Order
Library invoice types and sub-types allow for specialized rules and processing of invoices
Many-to-one purchase order to invoices (credit memo in a later release)
Prepayments
Deposit account
Payments charged to credit card
Pro-forma Invoicing
$0 invoices
Prorated additional charges
Payment requests process in US Dollar equivalency
Payment details from university financial (TBD)
Purchase order payment holds (remove hold)
Payment methods
Payment request (single purchase order or multiple purchase order)
Credit memo (single purchase order only in 1.6)
Note
To learn more about the Invoice document within OLE, see the Guide to the OLE Select and Acquire Module.
Electronic Resource Management covers all aspects of managing titles that are delivered or provided in electronic form. These materials might consist of e-books, e-journals, images, music, video, etc. Many of these resources are continuing serials while others, such as e-books, are one-time purchases. Managing electronic resources is highly complex because they are purchased and billed in many different ways – an institution may be purchasing a single journal title, an aggregated database with 5,000 titles that change throughout the year, or a journal package that contains 500 individual titles as well as several bundles with several titles each. In addition to purchasing workflows comparable to print counterparts, acquiring electronic resources may involve one (or more) trial periods for evaluation and generally requires complex negotiation of license and business terms. The workflow for making electronic resources accessible to patrons is difficult to manage because there is no physical item being tracked through a cataloging process. Electronic resources also require ongoing monitoring and management over their lifecycle to ensure continuous access in addition to workflows for disabling access to a resource no longer being licensed. While much work will still need to occur in future releases, OLE has taken some initial steps with an E-Resource Record in the 1.0 release, much more development will occur in the 2.0 release.
The E-Resource Record provides a place to store and view information about an electronic resource acquisition, including the title(s) involved and the content provider. Within the OLE user interface, the E-Resource Record presents a single, unified view of all information related to acquisition of an individual electronic resource or group of electronic resources, including titles, payment, licensing, administrative, and contact information. There are several general workflows that make up the electronic acquisitions process after a selector or patron requests the purchase of an electronic resource, these will be managed with the E-Resource Record.
Note
To learn more about the current functionality of E-Resources within OLE, see the Guide to the OLE Select and Acquire Module.
OLE created extensive specifications for the licensing process. Licensing is a variable step in the electronic acquisitions process. Some resources do not require a license at all and can be used within the guidelines of copyright law, while others require extensive negotiation of business and licensing terms. In lieu of a negotiated license, some vendors use standard Shared Electronic Resource Understanding (SERU) agreements to bypass complicated licensing processes. The goal of the licensing specifications is for a license editor that is flexible enough to encode the rights for a variety of scenarios making them easy to query, rather than recording the terms only for fully negotiated licenses. License Request e-documents, used to manage negotiations, are available in OLE.
Licensing Process in OLE:
Request a standard license from a publisher for a resource
Assign the license to a “shepherd” or license owner
Compare the license with standard requirements established by the institution and/or library
Back and forth negotiation with the publisher and library administration to modify license language if necessary
If approval, final signatures from both parties recorded
Storage of final license document (generally a PDF) in OLE
Coding machine-readable interpretation of license terms in OLE via a license editor (will be stored as ONIX-PL in the DocStore) will be available in a future release.
Note
To learn more about the current functionality of Licensing within OLE, see the Guide to the OLE Select and Acquire Module.